See Full Size
Coal use peaks as world warms
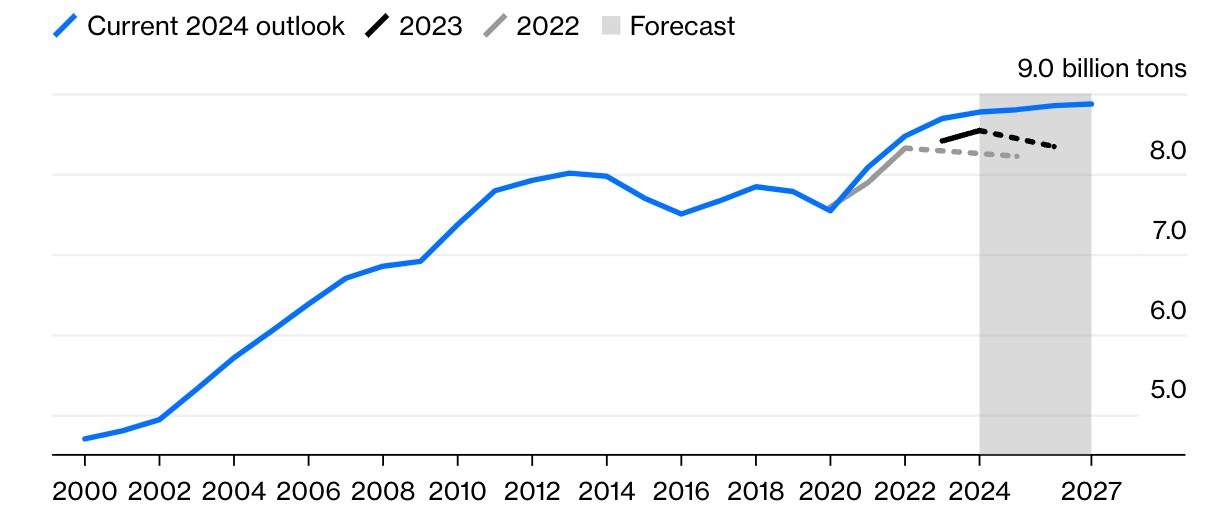
According to the report, coal use worldwide reached a new peak last year. increased to 8.7 billion tons. This level is expected to remain high for the next few years, according to the IEA. One of the main reasons behind this situation is the price increases in global gas markets following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. On the other hand, 2024 First year in which the 1.5 degree threshold was exceeded and at the same time hottest year It went down in history as.
See Full Size
The report states that most of the increase in coal demand Chinese ve India It was also emphasized that it was caused by Chinesefrom the rest of the world 30 percent It consumes more coal, and this year coal demand increased by 1 percent, reaching 4.9 billion tons. The country, which accelerates the construction of nuclear power plants and increases solar and wind energy capacities, aims to limit the increase in coal demand with these steps. It was stated that coal demand in India will increase by more than 5 percent to 1.3 billion tons.
Coal demand has already peaked in developed economies and is expected to continue declining until 2027. The European Union’s carbon reduction policies and the fact that natural gas is a cheaper alternative in the USA and Canada support this decline. The IEA states that coal-fired energy production will decrease by 5 percent in the USA and 12 percent in the European Union for 2024.
This news our mobile application Download using
You can read it whenever you want (even offline):