See Full Size
Antimatter rocket for space
Although today’s conventional rockets provide high thrust, they have serious efficiency problems. On the other hand, existing solutions such as electric propulsion or solar sails offer high efficiency but are very limited on the propulsion side. At this point, scientists suggest that the problems can be solved with rockets powered by antimatter.
See Full Size
These two types of reactions are most suitable
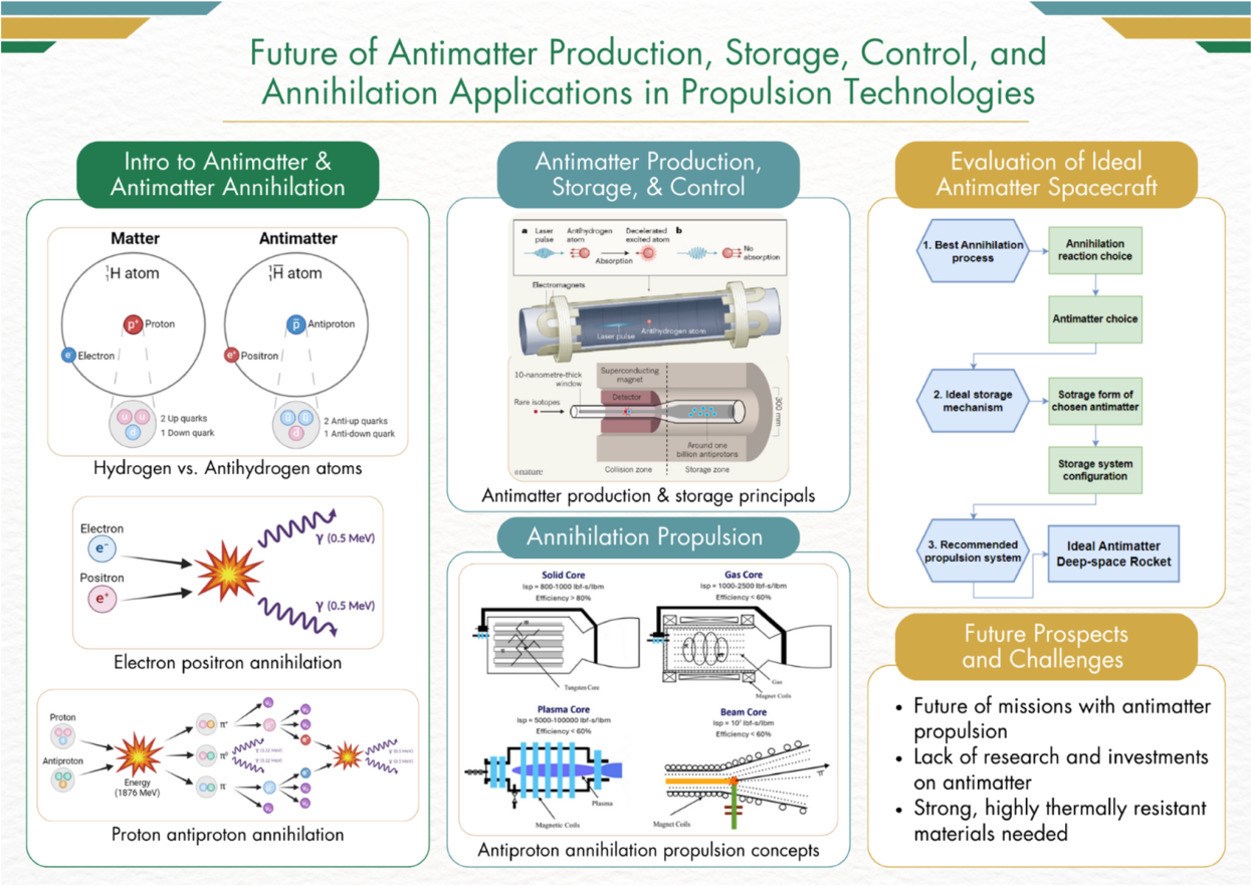
According to what is reported, antimatter consists of antiparticles. These antiparticles have the same mass as ordinary particles but opposite charges and quantum spins. When an antiparticle encounters its corresponding particle, they annihilate each other, releasing their combined mass as energy. This results in the most energetic reaction known in physics. In the research, scientists state that two types of antimatter reactions are especially suitable for space missions.
The first involves the interaction of antiprotons with nucleons, which include both protons and neutrons. Antiprotons are the antimatter counterpart of protons. When an antiproton encounters a nucleon such as a proton or neutron, both particles annihilate and tremendous energy is released. This reaction stands out with both its stability and high energy production. The second relevant reaction is the interaction of positrons with electrons. Here too, it is said that the reaction is stable and offers high energy efficiency.
The critical factor in choosing these reactions is that the antimatter particles can be stored safely on long-duration missions. Antiprotons and positrons meet this requirement.
300 times stronger than fusion
See Full Size
Researchers say a rocket powered by antimatter to 20 million meters per second states that it can provide a specific impulse of up to This represents the highest level of thrust ever imagined and is seen as a technology that could enable interstellar travel. With this speed Getting to Proxima Centauri in just 60 years possible. In addition, released from antimatter reactions 70 percent of the energy is direct thrust This makes these systems extremely efficient.
Fuel is difficult to produce
Despite all this exciting potential, antimatter fuel remains production, storage and cost still a big challenge. Current production methods fall far short of the quantities needed to propel spacecraft. At this point, it is the most promising type of antimatter. antihydrogen stands out. Antihydrogen is the simplest pure antimatter atom and attracts attention with its stability, long-term storage capacity and ease of production. However, large-scale production of antihydrogen is still under development. Researchers state that increasing this capacity is of critical importance for antimatter rockets.
Source
https://interestingengineering.com/space/antimatter-rocket-engine-300x-stronger
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666202724004518#abs0003
This news our mobile application Download using
You can read it whenever you want (even offline):