See in full size
Before moving on to the continuation of the article, the term “dark” we use here does not express a color and is a metaphor. “Dark” here is that the nature of these phenomena is still not known to a great extent and cannot be directly detected by observations.
In the past, astronomers, galaxy research conducted through two -dimensional images. Today, however, thanks to multiple object spectroscopy, the shift of galaxies to red, their distance and position can be mapped in three dimensions. Thus, it is possible to model the large -scale structure of the universe more accurately.
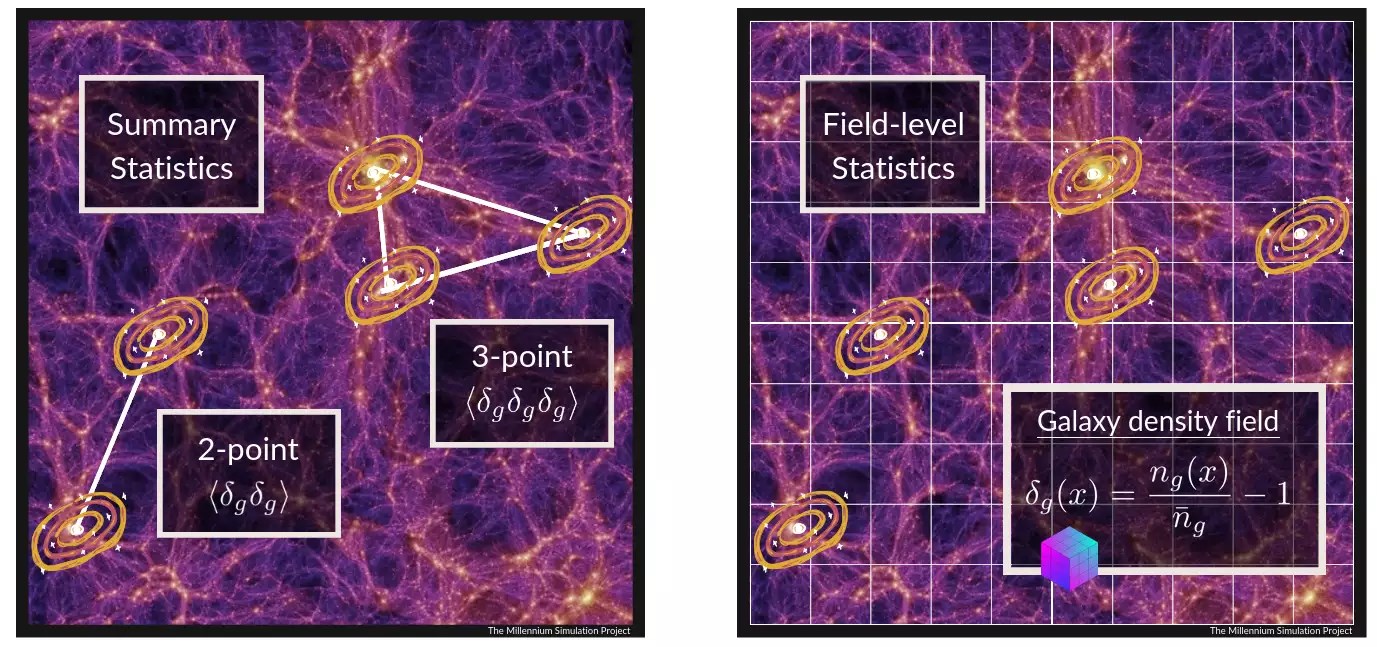
However, analyzing these three -dimensional data statistically requires great calculation power. Traditionally, these data are compressed by methods called “N-NOKTA CORRELATION FUNCTIONS”. But this is a jamThe scratching process can cause some critical information to be lost.
It became possible to analyze before the data is lost
See in full size
“We work directly with a 3D galaxy map in the field level, N Nguyen says. These maps are represented as a grill consisting of three -dimensional pixels on the computer. The FLI method predicts how this 3D structure should be in terms of dark matter and galaxy distribution, and tries to match these estimates with the observed galaxy positions.
Nguyen and his team tested the FLI method for the first time with a team at the Max Planck Astrophysics Institute in Germany, on the dark matter halo maps. These halto structures can be defined as clouds of dark matter that surround the galaxies and galaxy clusters. We can compare the halos to the skeletal structures in which the visible substance is transformed into galaxies.
More than 5 times more details can be achieved
The results are compared to the two and three point correlation functions of FLI analysis, old methods. Three to five times more details and accuracy He showed that he presented. So what does this secret information reveal? The large -scale structures of the universe, ie the huge chains of the galaxy clusters, can be monitored to the quantum fluctuations that occur during the large explosion. FLI may reveal asymmetry in these fluctuations. In addition, anomalies in the evolution of the galaxies in the early universe can provide new information about the dark matter or even help us better understand the gravity itself.
The next step will be tested with the data coming from the observations that will soon be launched and opened to move FLI’s success further. All of these new vehicles will carry out red slipping of galaxies. The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, which will be launched in 2027, is eagerly awaited for these research.
This news, Our mobile application download and download,
You can read at any time (even offline):